NASA once said, “Friendly reminder: We’re just a small speck in a massive universe!”
Have you ever stopped for a moment and pondered about this?
In the grand scheme of things (of space and time), we’re only specks of dust in this vast universe. It’s such an astonishing yet humbling thought at the same time.
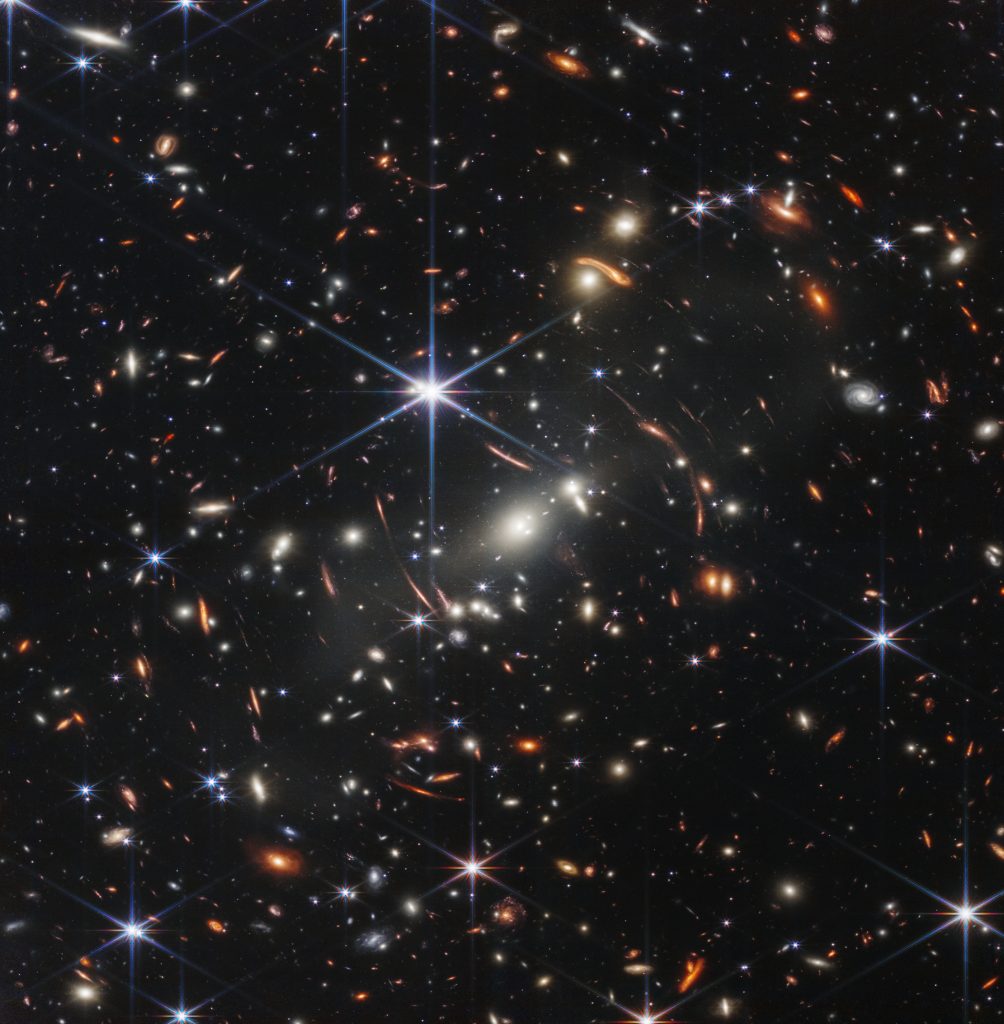
On July 12, 2022, NASA just unveiled the first set of images taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), one of which is the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723. The image showed thousands of galaxies, which amazingly only cover a small patch of sky, as small as a grain of sand, held by someone at arm’s length on the ground.

To better understand the scale of this image, try this.
Take a ballpoint pen and hold it at arm’s length (stretch your arms) in front of the night sky. Now, focus on its very tip while remembering there’s still the vast night sky in front of you.
The ballpoint pen’s tip—that’s what Webb Space Telescope captured. In other words, these thousands of galaxies we see are just tiny specks.
I have gathered some facts that will show how big space actually is.
In the following pictures, I will show you the comparison of our Earth to other plants and our entire system to others in the Universe.
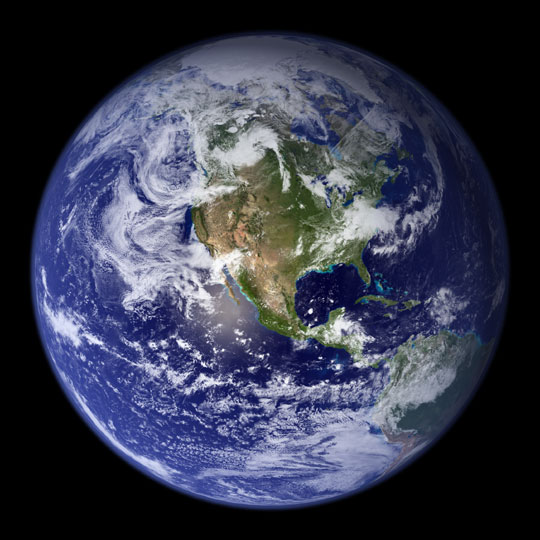
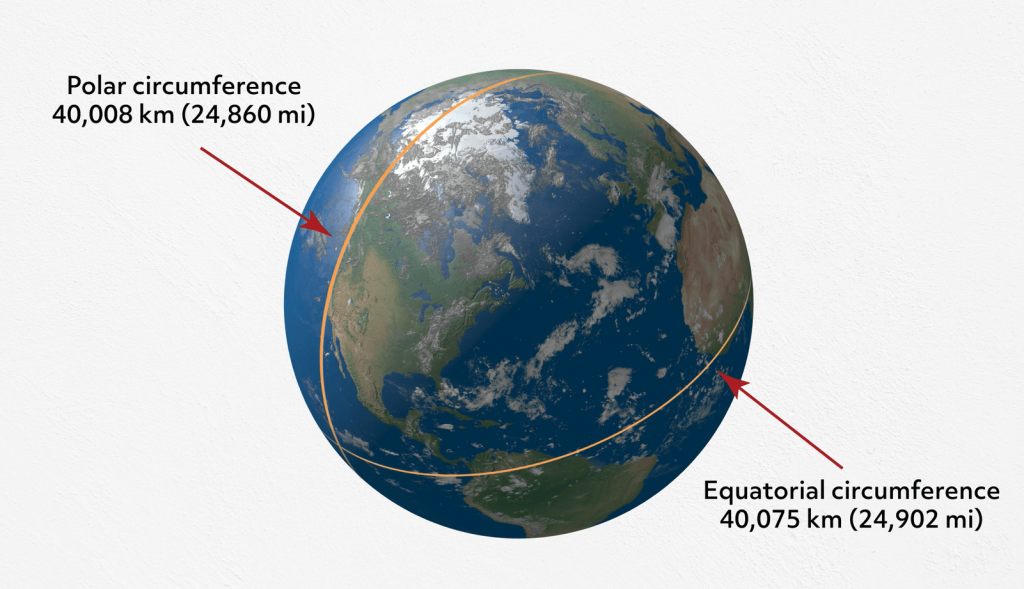
Here’s a photo of Earth, the planet on which billions of us people live. It’s the third planet from the sun and the fifth-largest planet in the solar system.

It has an equatorial circumference or the distance around the equator of the Earth of about 24,901 miles (40,075 km).
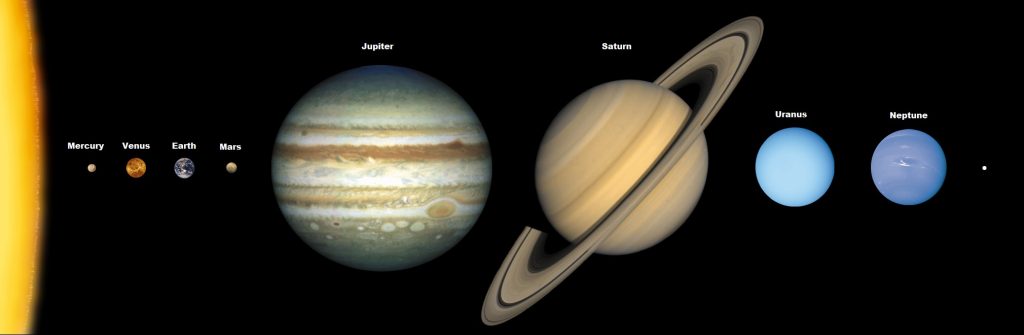
It may be a massive planet to us, but Earth suddenly looks smaller than other planets in our solar system.
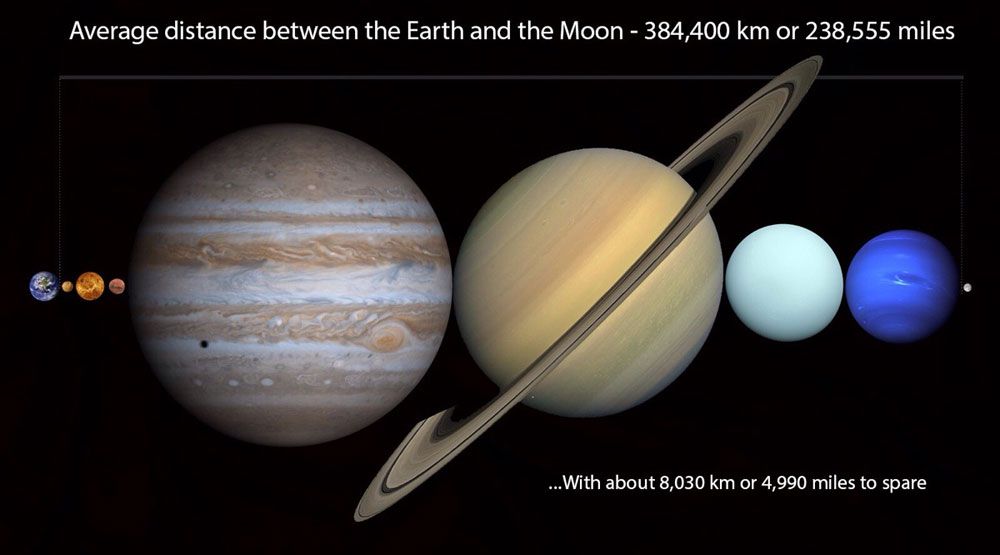
Now, this is how far the moon is from Earth. It’s about 38,855 miles (384,400 kilometers) away from our home planet.

But did you know you can fit all the planets in our solar system in that gap, the distance between Earth and its moon? Amazing, right?
Now, let’s compare Earth to the largest planet in our solar system, Jupiter.
See how tiny Earth is compared to Jupiter.
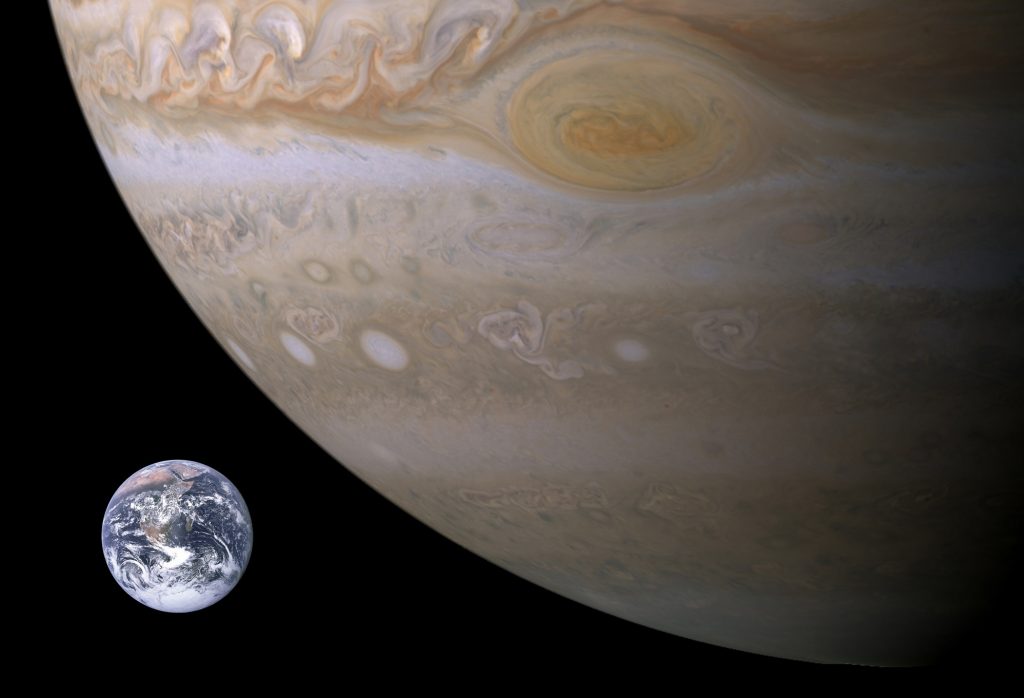

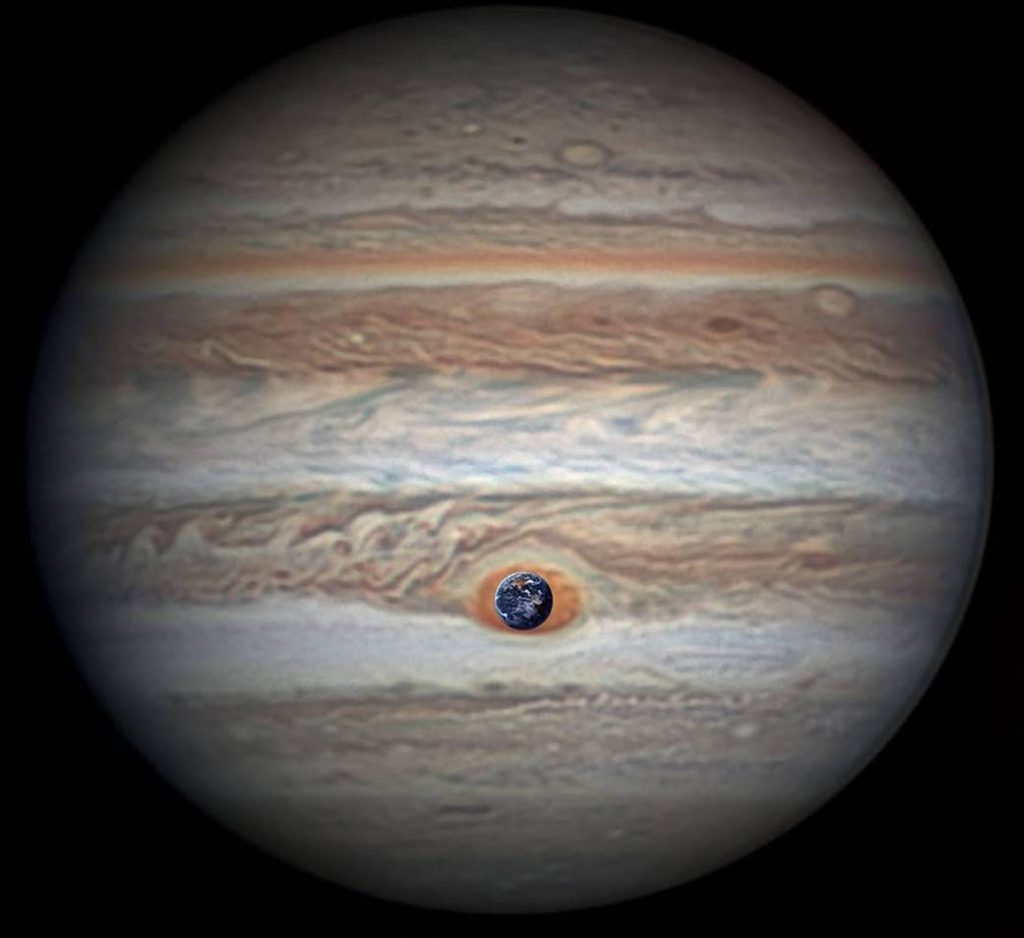
Another interesting fact is that the “Great Red Spot,” or the long-lived giant raging storm on Jupiter, could swallow the whole Earth. Also, about 1,300 Earths can fit inside Jupiter.

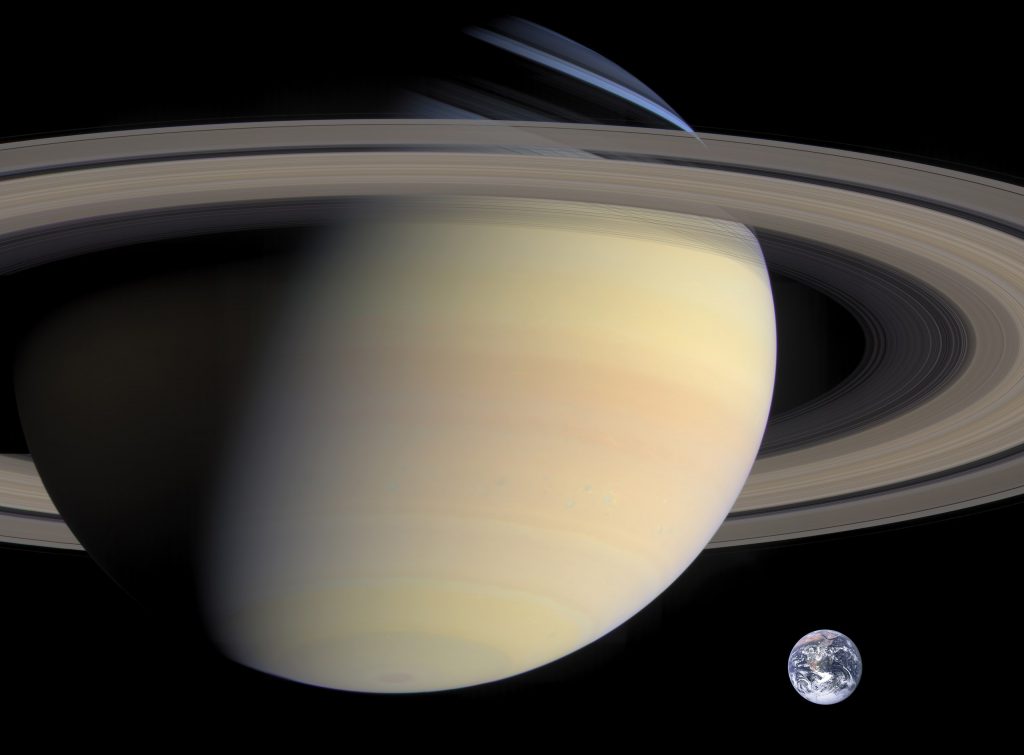
How about we compare Earth to Saturn, the second-largest planet in the Solar System after Jupiter?
Here you can see how big Saturn is compared to Earth.

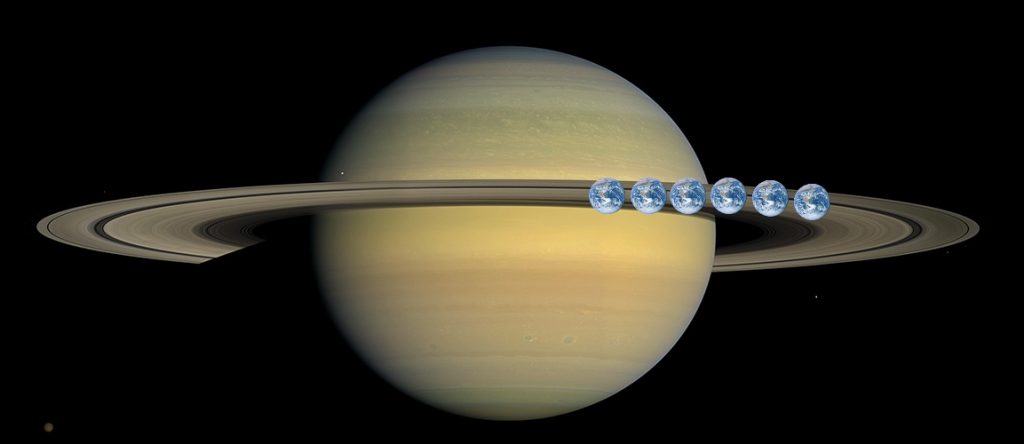
Here’s another photo about how six Earths would compare with Saturn. There’s still A LOT of room to spare, right?

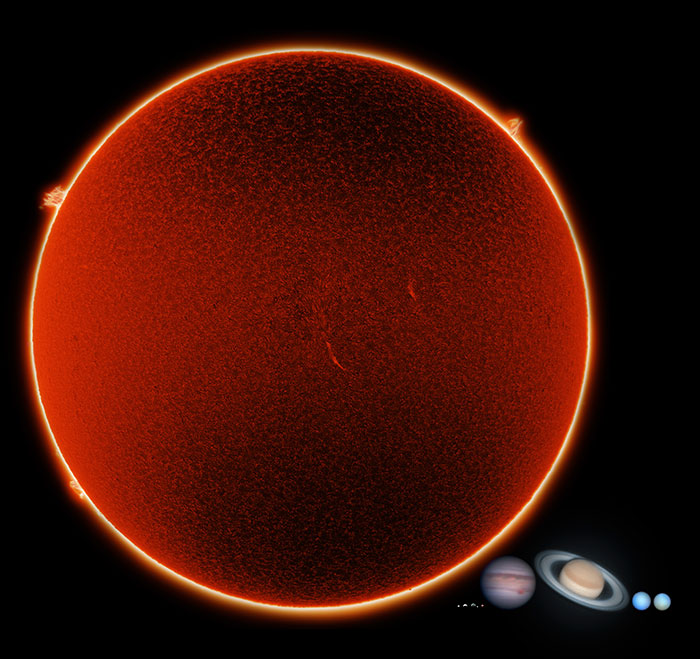
Now, it’s time to compare Earth with our Sun, which is the center of our solar system.
Our Sun is a yellow dwarf or medium-sized star, measuring about 864,000 miles (1.4 million kilometers) wide. It’s about 109 times wider than Earth.
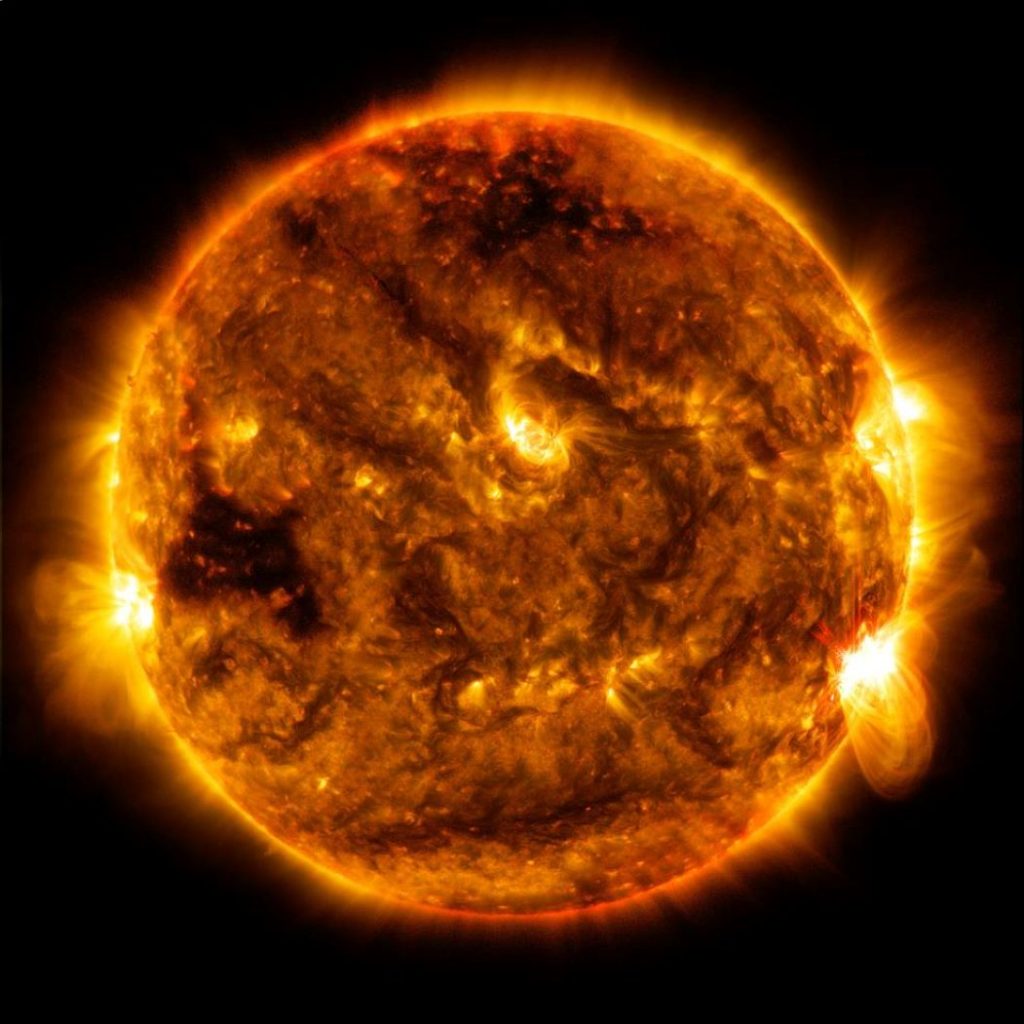

Here’s what Earth looks like next to the Sun. The solar flares or the tremendous explosions on the Sun look even bigger than our home planet.

Here’s an even better image comparing the Sun to other planets in the solar system.
But if we compare our Sun to other suns in the Milky Way galaxy, it’s inferior to them. Remember, our Sun is classified as a medium-sized star among these hundreds of billions of stars.
See how tiny the Sun is compared to other giant stars like Betelgeuse, Antares, Aldebaran, and Rigel, among others.
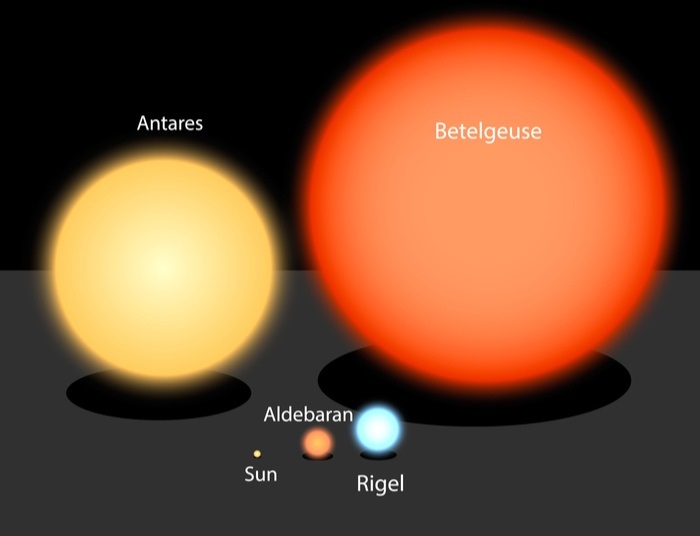
Betelgeuse, also known as Alpha Orionis, is a red supergiant star and the second brightest star. It measures 1.2341718 billion km in diameter and is approximately 764 times larger than our Sun.
If we were to think of the scale, about 1 quadrillion Earth could fit inside Betelgeuse. Imagine that!!
Now, let’s go even bigger. How about we compare our Sun to the largest star ever observed, UY Scuti?

UY Scuti is a variable red hypergiant star, measuring about 2.3765 billion km in diameter. To put that in perspective, almost 5 billion suns could fit inside the UY Scuti’s sphere.
To think that our Sun is the largest in our solar system yet is incomprehensibly small compared to other Suns! Just mind-blowing indeed!
The Sun is located in the Milky Way galaxy’s spiral arm, the Orion Spur, between two major arms (Perseus and Sagittarius).
Remember that the Sun is located in the Milky Way galaxy, with the planet Earth also located there.
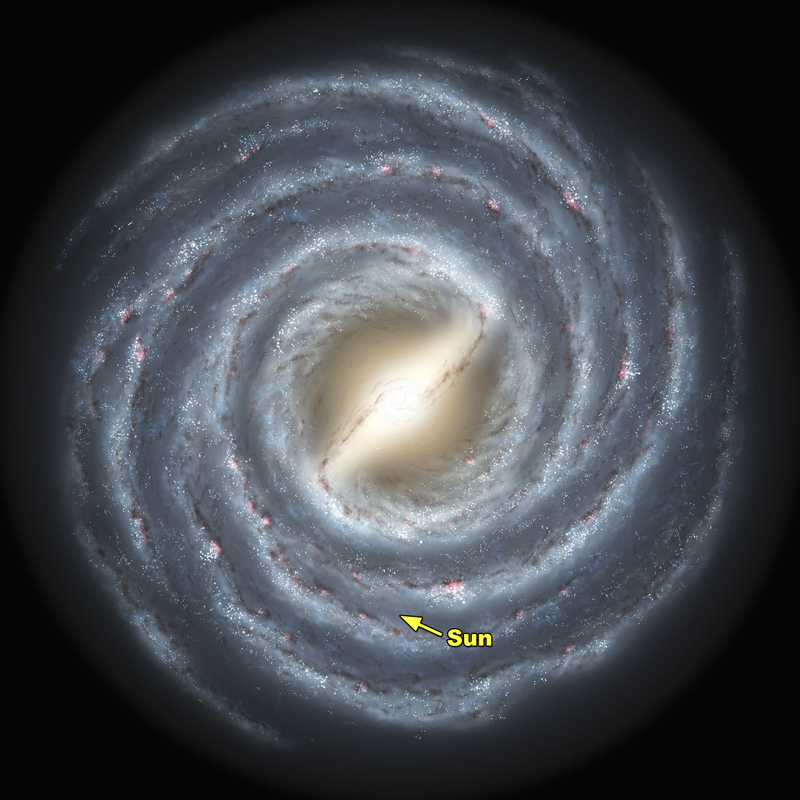

All the stars we see at night are just part of the tiny dot here.
But if we were to compare the Milky Way to our neighbor galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy or M31, it’s twice bigger than the Milky Way.
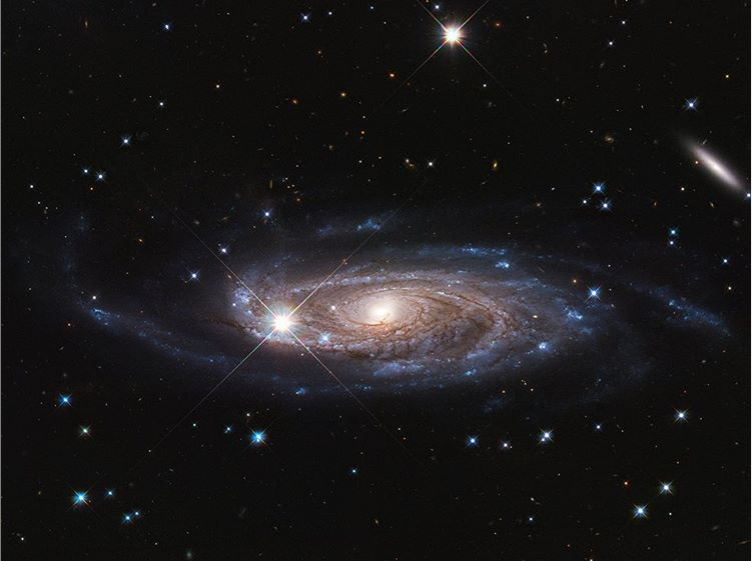

And to other existing galaxies in the universe like IC 1011, M87, and Andromeda, among others, the Milky Way galaxy is just a tiny blip.

To top the already overwhelming vastness of the universe, let’s go back to the image of thousand of galaxies taken by the Webb Space telescope. Remember that it’s just the size of a grain of sand, and this photo only covers a small patch of the entire sky!
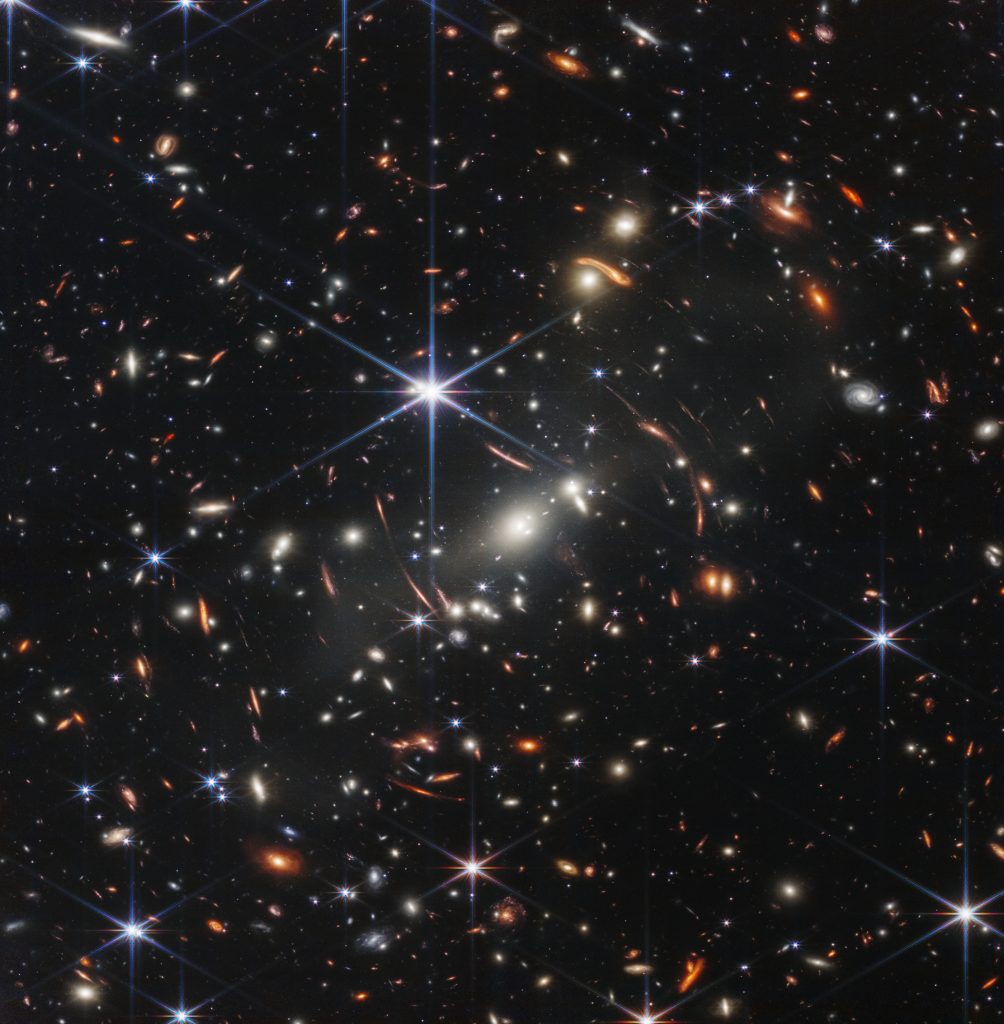

Think about the other galaxies. So far, the Hubble Space Telescope has revealed an estimated 100 billion galaxies in the universe, but this will likely increase as space technology improves.
These facts indeed show us how incredibly small we are in the universe. If thinking about all these doesn’t make your head hurt, I don’t know what else will!







