For more than 100 years, scientists have been studying global warming and its disastrous effects, one of our planet’s most critical issues.
From heat waves, severe storms and flooding, and increased drought to changing weather patterns, melting glaciers and warming oceans, rising sea levels, loss of species, and even health risks, these catastrophic effects of climate change are undoubtedly a threat to the world.

Thankfully, scientists have been working hard to address climate change and protect our planet. Through innovative research and groundbreaking technology, they explore ways to prevent the climate crisis from worsening.
A small but growing number of astronomers and physicists are a testament to that.
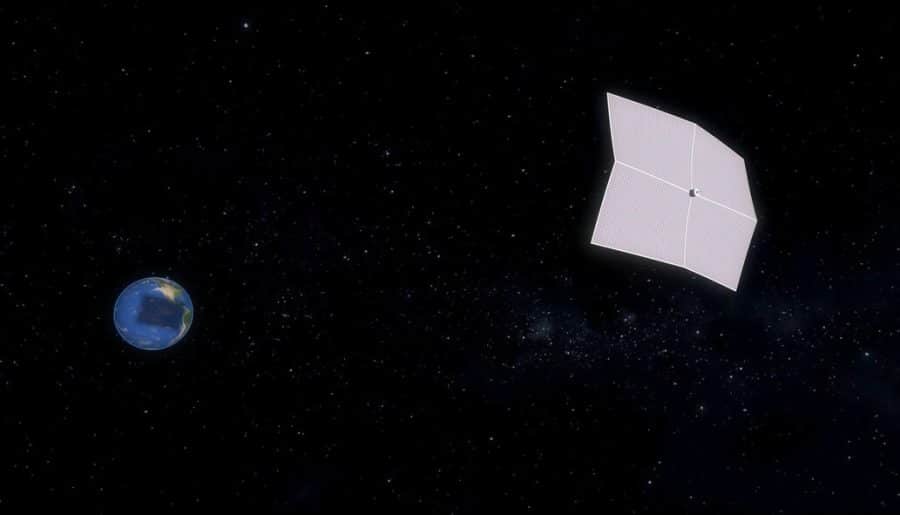
Did you know that a group of Israeli scientists propose a potential solution for the climate crisis: a giant parasol or “umbrella” that would float in outer space to block a portion of solar radiation?
Yes. You read that right!
The plan is to make a huge space-based sun shield and send it to L1, the Lagrange point between the sun and Earth. A Lagrange Point is a place in deep space where an object can stand very still with minimal energy. This will help block a small amount of solar radiation, which is important in fighting global warming.
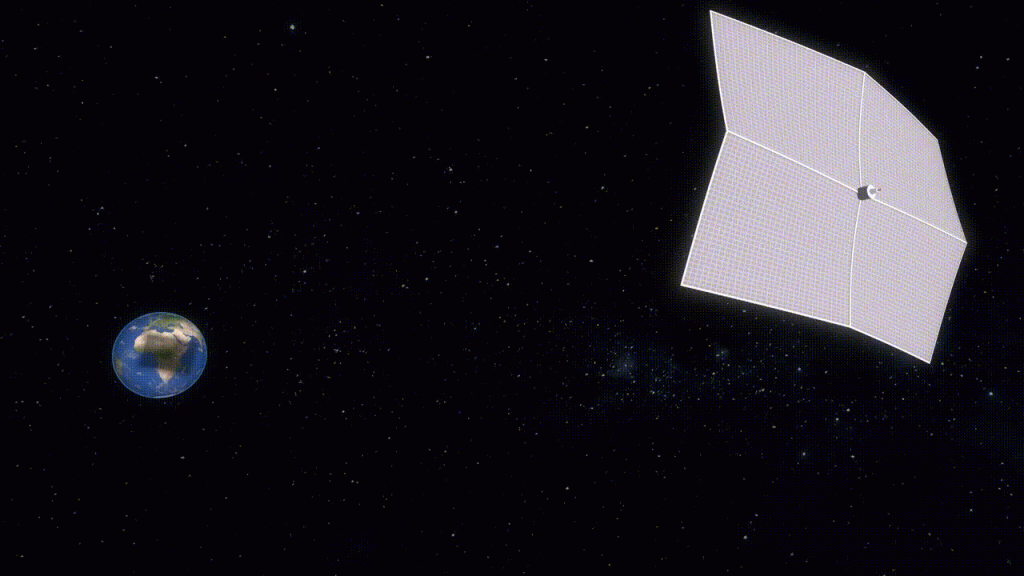
According to scientists, if we can block almost 2% of the sun’s rays, we can reduce the planet’s temperature by 1.5 degrees Celsius or 2.7 Fahrenheit.
By reducing the amount of sunlight that reaches the Earth, the planet could cool down rapidly, regardless of increasing carbon dioxide levels. This could help keep the Earth’s climate in check.
Now, you may ask, “Why do we need to reduce the amount of sunlight that reaches the Earth?”
The accumulation of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere leads to global warming. These pollutants absorb sunlight and solar radiation that normally escape into space after bouncing off the earth’s surface.

However, as the pollutants accumulate, they trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, which causes the Earth to become warmer. Another alarming thing is that these pollutants can remain in the atmosphere for years or even centuries.
István Szapudi, an astronomer at the University of Hawaii Institute of Astronomy, said, “In Hawaii, many use an umbrella to block the sunlight as they walk about during the day. I was thinking, could we do the same for Earth and thereby mitigate the impending catastrophe of climate change?”
According to scientists, a sun shield should be made of sturdy materials to remain in place and intact. It should also equal to 1 million square miles to prevent the sun’s harmful rays.
How big is that? It’s approximately the size of Argentina!
However, they acknowledge this proposed sun shield would weigh around 3.5 million tons, making it too heavy to launch into space. So, the only possible option would be to have several smaller shades.
These shades would not block the sun’s light entirely; instead, they would create a slightly diffused shade on Earth.
He also proposed attaching a large solar shield to a captured asteroid. This would likely reduce the shield’s weight to only 1% of its total weight, around 35,000 tons.
Unfortunately, even this smaller shield is too heavy for a rocket to lift, as the largest rockets can only lift about 50 tons to low Earth orbit.
However, Szapudi’s study suggests that the shield’s mass can be reduced even further with improvements in lighter materials.

But some people disagree with using a sunshade to combat climate change, including Susanne Baur, a researcher in France.
Baur believes installing the sunshade would be too expensive and time-consuming, considering how our planet is warming fast.
She also thinks that if a solar storm or space rocks damaged the shield, it could lead to a sudden increase in temperature, which would be disastrous. Instead, we should focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and removing carbon dioxide from the air to address the climate crisis.
However, those who support the sunshade idea argue that reducing greenhouse gas emissions won’t be enough.
Removing carbon dioxide from the air is challenging, so it’s essential to consider all potential solutions.
The researchers who proposed the giant parasol said they are prepared to create a 100-square feet sample shade and require funding of about $10 million to $20 million for the demonstration.
The team is currently in the initial planning phase, but they can release a test model within three years if they get enough funding.
They also estimated that a full-scale version of the project would be quite expensive, costing trillions of dollars. However, researchers believe the project could reduce global temperature by 1.5 degrees Celsius in just two years.







